Hydroxyethylcellulose(HEC) sounds complex, but is it really? It’s a mouthful, but let’s break it down. Think of it like a helper in many products, but it can be confusing.
Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer derived from cellulose. It acts as a thickener, binder, and stabilizer in various applications. It’s made by reacting cellulose with ethylene oxide. HEC is commonly used in paints, cosmetics, and construction materials.
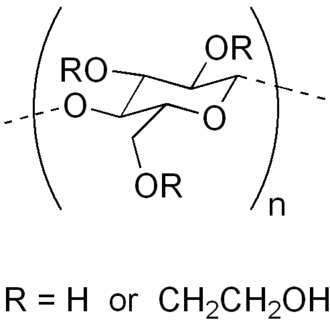
That’s the short answer, but we’re just getting started. There’s much more to HEC than that simple definition. Let’s dive in and learn some new knowledge together!
What is hydroxyethylcellulose used for?
HEC seems useful, but where is it actually used? You might be surprised at how many products include it. Will it show up in your daily life?
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is a versatile ingredient. It finds its place in a wide range of applications, including paints, coatings, adhesives, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals. In these products, it works as a thickener, stabilizer, and water-retention agent. It helps give things the right texture!

Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is like a secret ingredient that is used in a many of common products. Jinghong, as a leading manufacturer, offers HEC that boasts excellent thickening, dispersibility, and stability. Because of this, you will find it in latex paints, it creates a good workability. Also you will find it in construction materials and even oil drilling!
| Application | Function of HEC | Jinghong HEC Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Latex Paints | Thickener, stabilizer, dispersant | Excellent thickening, stable effect, good workability |
| Construction | Water retention, retarder, adhesive | Improves workability, water retention |
| Oil Drilling | Thickening, fluid loss control | Provides stable performance in harsh conditions |
| Personal Care Products | Thickener, binder, film-former | Provides smooth texture, good compatibility with skin |
| Pharmaceuticals | Binder, controlled-release agent in tablets | Ensures uniform drug release, safe for consumption |
Jinghong HEC has a lot of product models, and customers can choose the right model according to their formula. It is also a kind of non-ionic cellulose, so it has good compatibility with other materials.
What are the disadvantages of hydroxyethyl cellulose?
HEC sounds great, but is it perfect? Does it have any downsides, or any situations where it shouldn’t be used? Are there any risks involved?
While HEC is generally safe, some potential issues exist. It can be sensitive to microbial attack, requiring preservatives. High concentrations may also lead to excessive thickening. But these are not common.
Though widely used, HEC is a water-soluble polymer and is susceptible to biodegradation. Which may affect the shelf life of end products. Therefore, preservatives need to be added to maintain a long storage life.
| Disadvantage | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Microbial Degradation | HEC can be broken down by microorganisms, affecting product shelf life. | Use of preservatives, proper storage conditions. |
| Excessive Thickening | High concentrations can lead to overly thick solutions. | Careful formulation, using the appropriate HEC grade and concentration. |
| Sensitivity to pH | HEC’s performance can be affected by the pH of the solution. | Maintaining optimal pH levels through buffering agents. |
| Potential for Air Entrapment | During mixing, HEC can trap air, leading to foam formation in some applications. | Use of defoamers, proper mixing techniques. |
| Cost | Compared to some synthetic polymers, HEC can be more expensive. | Optimization of formulations to use the minimum effective amount, explore alternatives. |
As a cellulose, HEC needs careful handling during manufacture and storage. Jinghong has great and strict testing process, and all indicators meet the national standards. So the quality is good.
What is the difference between carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl cellulose?
We’ve talked about HEC, but what about CMC? You might have seen "carboxymethyl cellulose" and wondered how it compares. Are they used for the same things?
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) are both cellulose derivatives, but they differ in their chemical structure and properties. CMC is anionic (negatively charged), while HEC is non-ionic (no charge). This affects their compatibility with other ingredients.
The main difference is their charge. CMC’s anionic nature makes it more reactive with certain materials, while HEC’s non-ionic nature makes it more compatible with a wide range of formulations.
| Feature | Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) | Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Charge | Anionic (negatively charged) | Non-ionic (no charge) |
| Solubility | Water-soluble, forms clear solutions | Water-soluble, forms clear solutions |
| Thickening Efficiency | Generally higher than HEC | Moderate to high, depending on the grade |
| Salt Tolerance | Lower; can be affected by high salt concentrations | Higher; more stable in the presence of salts |
| pH Sensitivity | More sensitive to pH changes | Less sensitive to pH changes |
| Applications | Food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, industrial | Paints, coatings, personal care, construction, oil |
| Main Functions | Thickener, binder, stabilizer, emulsifier | Thickener, stabilizer, water-retention agent |
Jinghong currently does not produce CMC, but has a large-scale factory producing HEC, MHEC,RDP and other products. Because of that, we have great control over the quality and a stable supply.
What are the pharmaceutical uses of carboxymethyl cellulose?
CMC is used in a lot of pharmaceutical products, but why? What properties make it perfect for this application? Why is it used in medicine?
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is used as a binder, disintegrant, and controlled-release agent in tablets and capsules. It helps hold the ingredients together. It can also affect how quickly a drug is released in the body.
CMC is useful because it’s safe for people and it can create gels. This lets it manage how drugs are released, creating medicines that release their contents quickly, or slowly.
| Pharmaceutical Use | Function of CMC | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tablet Binder | Holds the active ingredients and excipients together in a tablet. | Provides tablet hardness and integrity. |
| Tablet Disintegrant | Helps the tablet break down into smaller particles when it contacts water. | Facilitates rapid drug dissolution and absorption. |
| Controlled-Release Agent | Forms a gel matrix that slowly releases the drug over time. | Provides sustained drug release, reducing dosing frequency. |
| Suspending Agent | Helps keep solid particles dispersed in liquid formulations. | Ensures uniform drug dosage in suspensions. |
| Thickening Agent | Increases the viscosity of liquid formulations. | Improves the texture and stability of liquid medications. |
| Film-Forming Agent | Creates a thin, protective film on tablets or other solid dosage forms. | Improves the appearance and swallowability of tablets, protects from moisture. |
| Emulsifier | Stabilizes emulsions by preventing the separation of oil and water phases. | Enhances the stability and appearance of emulsion-based medications. |
Jinghong does not currently produce CMC, but its HEC product has a wide range of product models, and customers can choose the right model for their needs.
Is HydroxyEthyl cellulose organic or inorganic?
Finally, a basic question: Is HEC organic? You might be wondering about the source of this material. Where does it really come from?
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is considered an organic compound. This is because it is derived from cellulose, a naturally occurring polymer found in plants. It’s based on carbon, which is the main element of an organic compound.
Even though HEC undergoes chemical modification, its backbone is still based on the organic cellulose structure. So, it’s classified as an organic compound.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin | Derived from cellulose, a naturally occurring polymer found in plants (mainly wood pulp and cotton). |
| Chemical Structure | Contains carbon-hydrogen bonds, the defining feature of organic compounds. |
| Modification Process | Cellulose is reacted with ethylene oxide, introducing hydroxyethyl groups, but the base structure is organic. |
| Classification | Considered a semi-synthetic polymer because it is derived from a natural source and modified chemically. |
| Biodegradability | Can be biodegraded by microorganisms under certain conditions, typical of many organic compounds. |
Jinghong’s HEC is derived from high-quality cellulose sources, ensuring a reliable and consistent product. As a company based in China, we prioritize quality control, certifications, and reliable logistics.
Conclusion
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is a very useful organic compound derived from cellulose. It is widely used for thickening, stabilizing, and water retention. HEC is a really useful chemical in many fields!



